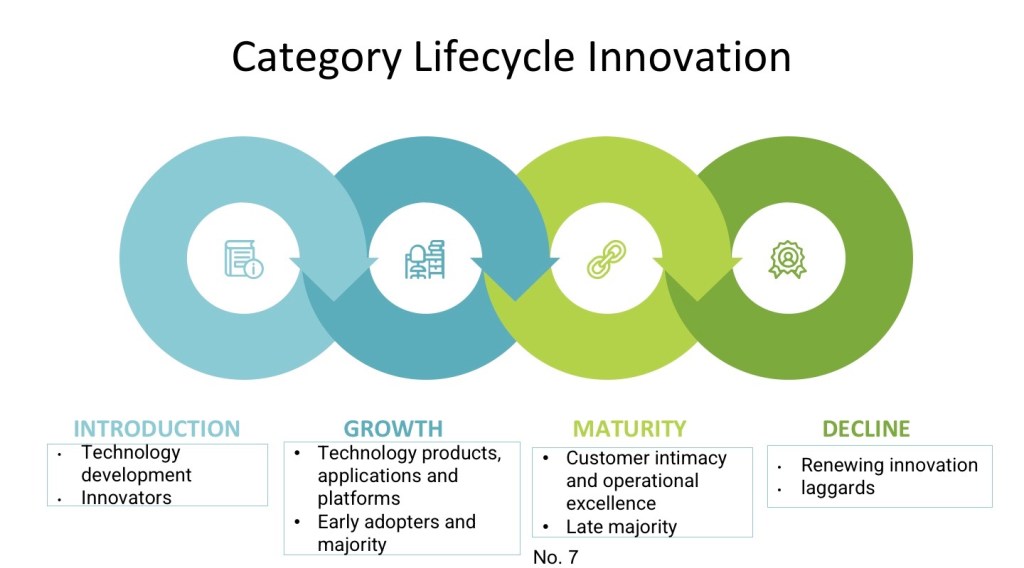
Any product lifecycle consists of four key stages, introduction, growth, maturity, and decline, and is a powerful tool to demonstrate the progress of new products from launching to discontinuance and replacement by successor products. Likewise, the lifecycle of the technology innovation begins as a researched technology, then a breakthrough technology, to technology products and applications, platforms, and services, all the way to its replacement by new innovative technology. In this article, I show the different categories of lifecycle innovations and how they progress and work.
Overview of the category lifecycle innovation
In Moore’s book ‘Dealing with Darwin’, 2005, he argued the types of innovation in line with the technology diffusion lifecycle and grouped them into four zones as per the following (Moore, 2005)1:
Product leadership zone
According to the technology diffusion lifecycle model, product leadership occurs during the introduction and growing phases. Products leadership are new products and values that are: (1) disruptive innovations (e.g., new technologies, new products and services, applications, and platforms), (2) diffused by visionary techies (i.e., especially for new technologies), (3) by early adopters (i.e., for new products and applications) and (4) by the early majority, mainly for technology platforms. These innovative products are desirable (wanted by customers), risky to succeed, expensive, new to the market, and target non-existing customers and high-end markets. Therefore, the product zone is better executed in high-growth markets to enable producers to make reasonable returns that compensate for higher associated risks and win market share. For example, the invention of the internet in the early 1990s was considered a technological breakthrough, and businesses like social media, digital media (music, film) and telecommunication are all successful applications of the discovery of internet technology.
Customer intimacy zone
This zone occurs during the late growing and the early mature phases led by late majorities or conservatories. Intimacy offerings are mainly incremental innovations aimed at enhancing customer experience, sustaining growth in the market, and strengthening market position or competition. Customer zone includes (1) line-extension innovation (e.g., introducing new sub-categories within existing offering products, examples are small cars), (2) enhancement innovation (i.e., modification or feature enhancement to an existing offering like Teflon coating for pans or higher pixel ratings for digital cameras), (3) marketing innovation (i.e., uses new or highly effective marketing campaigns or channels or pricing models to outperform competitors), and (4) experiential innovation (i.e., adding a service to an existing product to enhance, for instance, product trials, payment methods, post-sale services, or customisation). These innovative products are less risky, less desirable, and target existing markets, but can give a company a reasonable return through cost reduction, differentiated offers and efficiency savings. This innovation zone is better suited for mature and stable markets.
Operational excellence zone
This zone occurs during the late growing and mature phases led by the late majorities or conservatories. The operational activities are incremental innovations aimed at increasing corporate efficiency and reducing costs. This zone includes (1) value engineering innovation (i.e., optimizing parts and the overall assembly/creation process to reduce cost and improve market lead time), (2) integration innovation (e.g., when a selling price is discounted because of simplification or consolidation of a product), (3) process innovation (i.e. reduce the production cost by cutting the wastes and times required for production), and (4) value migration innovation (i.e., move away from the value-chain commoditized to segments which are richer in profit and growth opportunities). Like Customer Intimacy, the operational excellence zone is less risky and less desirable, but it can give the company money back through cost and efficiency savings.
Category renewal zone
This zone occurs during the declining and ending phases led by laggards. Renewal-zone products aim at reducing the rate of the growth-contraction by promoting: (1) organic renewal (i.e., resulting from internal resources to enterprise), (2) acquisition renewal (i.e., resulting from external resources to enterprise like merging and acquisition), and (3) harvesting or exit activities (e.g., closes out a line of business).
How do lifecycle innovations work?
Here is a brief description of the flow of the lifecycle innovations:
- Researched technology: Every technology innovation begins as a research project to expand knowledge on solving complex issues. And the outcomes of this initial stage are solution proposals or theoretical prototypes, yet the solution proposed is not ready for commercial. The key players of this stage include universities, research and development centres, and labs.
- Breakthrough technologies: this is the stage of introducing new technology to the market by techies. Techies are technology developers who buy researched technologies and transform commercial technologies; however, these newly born technologies require massive investments, business vision, higher risk, and time to reach market streams. A good example of this stage is the introduction of internet technologies in the early nineties and the Model-T assembly mass production of Ford Co. early nineteenth century.
- Technology products and applications: at this stage, entrepreneurs or so-called visionaries take the technology developed in the previous stage from techies and transform them into commercial products and applications that are more applicable to the company and individual needs. However, visionaries will face a big chasm (gap or barrier) to cross to reach the market streams. To cross this chasm and reach market streams, innovators will need to further develop these technology products and applications and transform platform products like digital mobiles, where many value-chain suppliers contribute to the development of digital mobile, along with articulating a marketing strategy capable to meet the customer expectations.
- Technology platforms: as explained in the previous stage, platforms are technology products contributed by multi-value chain suppliers, like automobiles, computers, mobiles, etc. These platform products are developed by the early majority and are aimed to reach the market streams. Companies involved in platform production will witness higher growth followed by a slowdown in sales due to fierce competition, causing those companies to reach maturity.
- Customer intimacy and operational excellence innovations: companies reached maturity and slow growth due to competition will make what is so-called customer intimacy and operational excellence innovation to sustain their market shares. Customer intimacy innovations involve product extension and enhancement, increasing customer experience, and marketing offers. And the operational excellence innovations include increasing operational efficiency to reduce waste and costs.
- Renewal innovations: when technology innovations reach the maturity and declining phases, innovation companies may seek organic growth (e.g., focusing on increasing sales) and external growth (e.g., acquisition and merging) to renew their businesses. However, technologies reaching this stage are expected to discontinue and be replaced by new ones soon.
- This post is sourced from my new book- Your Guide To Reach Innovation.
- For more information about the book: https://growenterprise.co.uk/your-guide-to-reach-innovation/
- To register in our newsletter: http://eepurl.com/ggcC29
Final note: the book- Your Guide To Reach Innovation, is an actionable guide to innovation from beginning to end. Enjoy reading the book, and I look forward to your reviews.
Author: Munther Al Dawood
maldawood@growenterprise.co.uk
References:
- Moore, G., 2005. Dealing with Darwin, Penguin Group, New York.
